New Development on Shape and Surface Texture as Supplementary Information
It has been discovered from many classification experiments that
certain kinds of produce do not distinguish from each other very well
by color spectrum alone. For example, between yellow squash and banana, or
even lemon.
To improve the classification rate of our color spectrum based
system, we have investigated many different ways of getting
shape and surface texture information.
-
 Shape estimation using bar-code scanner
Shape estimation using bar-code scanner
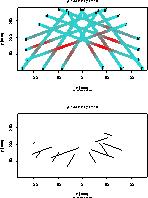 full size image
full size image
 full size image
full size image
-
 3D image reconstruction using a laser scanning device
3D image reconstruction using a laser scanning device
Here is the diagram of the system for taking slices of laser scans of
an object for reconstructing 3D image and
an example of the image taken from the laser scanning device (to find
out what the object is, click on the full size image).
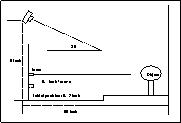 full size image
full size image
 full size image
full size image
-
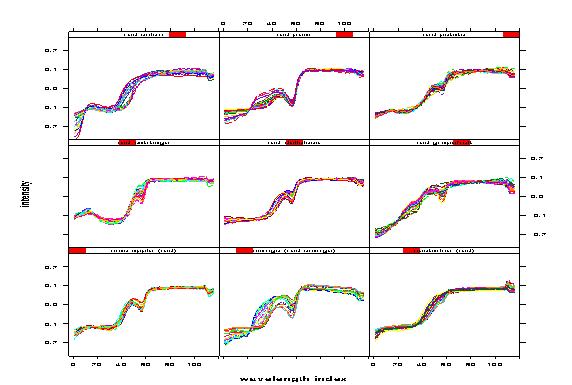
 Texture
Texture


-
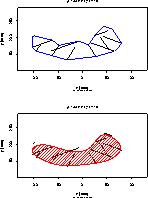
 Shape outline estimation
Shape outline estimation

We have developed a backlighting scheme for measuring the outline of
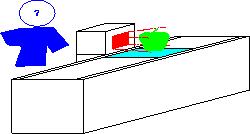
multiple objects in a plastic bag. The interference from the bag, which
is normally caused by specular reflection is
minimized when backlighting is used.
An outline tracing algorithm is developed to estimate the shape of
"partial" objects through convex polygon approximations.
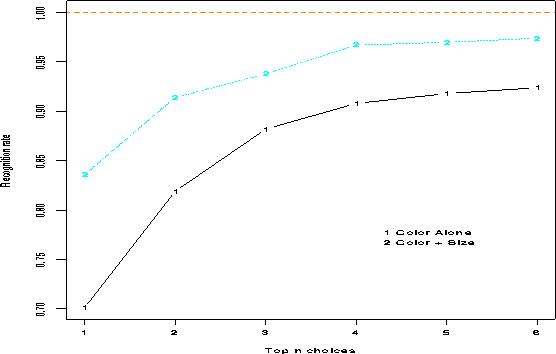
Some preliminary classification results showed significant improvement
in identification accuracy when the size information is incorporated.
Business Unit Interaction
Don Sun
and
Mark Hansen
at the Statistics research department
have been working closely with researchers in the physics
area at Bell Labs and engineers at NCR in Atlanta.
The major role of our statistics group is to develop
new methodologies and
algorithms for fruit identification and
provide guidance in improving the current apparatus to achieve more
accurate and robust result.
Gordon Thomas, Doug Rapkine, Harold Hess and Robert Chichester
at the physics departments in Bell Labs are mainly working on the
hardware design of the fruit recognition system.
Ron King, Don Collins, Jeff Treptau
etc. are our major
collaborators at NCR in Atlanta. Their major role is to build
prototype instrument, collect data, and carry out field testing.
Impact
The impact of this technology on the retail business is very
significant. It will help NCR to gain competitiveness and market
share in the industry of retail checkout device.
Current Status
Most of the research results on color spectroscopy
have been successfully transferred to NCR (Atlanta), where prototype
models are being built and tested.
A patent on the fruit classification based on color spectrum is being
filed by Lucent Technologies.
The research on incorporating shape information to improve the
performance of the existing color spectrum based system is still in
progress, and the work is being carried out under agreements between
Lucent Technologies and NCR on yearly basis.
The fruit recognition project greatly influenced our methodological
research in image analysis and recognition area. We have been
developing algorithms in estimating shape of objects from general
purpose laser scanning devices, which can have many different
applications in industrial imaging. The method of combining
different features together to perform sequential classification will
provide a very useful tool for many pattern recognition problems.
Back to the Statistics project page.
Back to the Statistics home page.
Last modified: $Date: 2000/11/02 21:14:27 $
dxsun@research.bell-labs.com
 Nearest neighbor method
Nearest neighbor method








